Introduction: Why RNG Source Matters in Crypto Gaming
Random Number Generation (RNG) is the backbone of fair play in crypto games—whether drawing cards, rolling dice, or spinning slots. But not all RNG is created equal:
- On-chain RNG uses transparent blockchain data or verifiable randomness functions.
- Off-chain RNG relies on external systems, like centralized servers or oracles.
Players must understand the risks of manipulation and how to verify outcomes. Read on to learn what makes each method different, how they impact fairness, and how to spot trustworthy implementations.
1. What Quality Randomness Requires
True randomness should be:
- Unpredictable — outcomes can’t be foreseen
- Unbiased — every result is equally likely
- Verifiable — users can audit the process
- Tamper-resistant — no one can influence the output post-fact
On-chain solutions, especially those using verifiable randomness, deliver these properties better than traditional methods. ([turn0search11])
2. Off-Chain RNG: The Traditional (and Riskier) Approach
Off-chain RNG generates random numbers using external servers or hardware devices and pushes results to a blockchain or game. Common methods include centralized server generation or oracles like Oraclize (Provable).
Risks include:
- Trust issues: Full confidence in the RNG provider is required.
- Manipulation or delay: Providers might alter outputs or introduce latency.
- Proof difficulty: Verifying integrity is often impossible.
While off-chain is easier to implement, it lacks transparency—making it hard for players to confirm fairness. ([turn0search4])
3. On-Chain RNG: Transparency and Verifiability
On-chain RNG harnesses blockchain data and cryptographic techniques to generate and verify randomness with high transparency.
Common methods:
- Blockhash-derived randomness: Uses recent blockhash as entropy. Easy but vulnerable to miner manipulation. ([turn0search4])
- Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function): Produces provable randomness via off-chain oracle with on-chain verification, preventing tampering. ([turn0search1], [turn0search5])
- Built-in randomness beacons: Some chains (e.g., Flow) offer native randomness generation to smart contracts. ([turn0search7])
- Secret-VRF (Secret Network): Generates randomness using SGX enclaves and Tendermint consensus for strong on-chain security. ([turn0search9])
These methods provide provable fairness, making it possible to verify outcomes independently.
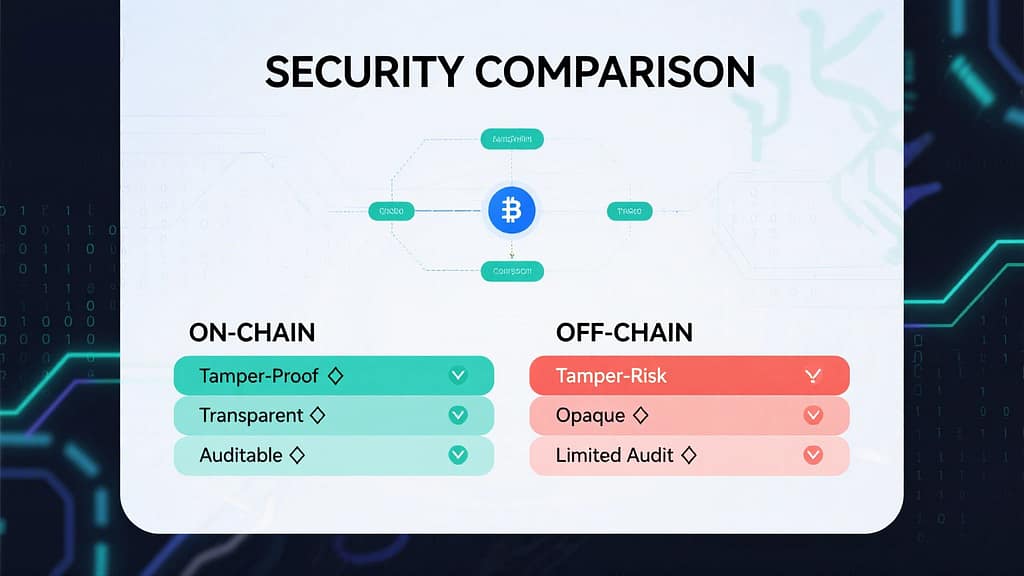
4. On-Chain vs Off-Chain: Side-by-Side Comparison
| RNG Type | How It Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Off-Chain RNG | Central server or oracle generates random number, sends to chain | Easy to implement | Requires trust, opaque, vulnerable to tampering |
| Blockhash RNG | Uses previous block’s hash as entropy | Fully on-chain, no external dependencies | Miner bias, weak entropy, reorg risk |
| VRF (e.g., Chainlink) | Oracle computes randomness + proof verified on-chain | Verifiable, tamper-resistant, crypto-secure | Slight delay, dependency on oracle infrastructure |
| Native Beacon (e.g., Flow) | Blockchain provides randomness for each block | Fully decentralized and predictable | Limited to supporting chains |
| Secret-VRF (SGX) | Uses SGX enclave + consensus for randomness | High security, tamper-resistant | Complexity, limited to specific chains |
5. Why On-Chain RNG Generally Wins
On-chain solutions improve fairness and transparency by providing:
- Auditability — you can independently verify each outcome
- Tamper resistance — miners or server operators cannot bias results
- Trustlessness — fewer external dependencies, especially with VRF or native beacon methods
6. How Players Can Verify Randomness
To check an RNG method:
- Identify the RNG type — check game documentation or UI (VRF, blockhash, etc.).
- Look for proofs — for VRF, verify that the cryptographic proof is available on-chain.
- Test any on-chain randomness — run through the verification steps if specified.
- Avoid opaque RNG systems — steer clear of platforms with no provable mechanism or unclear RNG sources.
7. Summary: Choosing Fair Crypto Games
- Prefer games using VRF or native on-chain randomness — they offer better security and verifiability.
- Avoid obscure off-chain RNG unless backed by strong proof of fairness.
- Always verify game documentation and look for transparency in mechanics.







